Understanding Bed Bugs (Cimex lectularius): Their Life Cycle, Eggs, and Where They Nest
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are resilient pests that thrive in homes and public spaces. These elusive insects can cause itchy bites and discomfort. For successful eradication, it is crucial to understand their life cycle, where they lay eggs, metamorphosis and where they nest.

Need Help Getting Rid of Bed Bugs?
Pest Dominion offers professional bed bug eradication and BPCA bed bug control services across Slough and surrounding areas. Our bed bug experts use proven, safe, and discreet methods for lasting results.
📍 Contact Pest Dominion today
📞 07999 936075 | 03308 224460
Don’t wait — get rid of bed bugs before they spread further. We guarantee discreet, reliable, and long-term results.

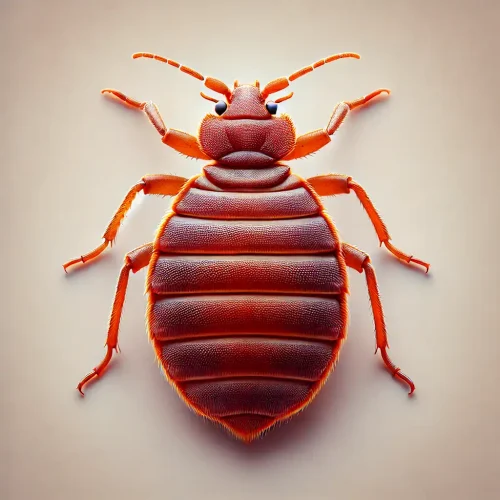
What are bed bugs?
Small, flat, wingless crawling insects that feed on blood. They’re about the size of an apple seed, reddish-brown, and grow plump after feeding. While they don’t fly, bed bugs are excellent at crawling and hiding in cracks and crevices, making them difficult to detect.
Eggs: The Start of the Cycle
Eggs are tiny, about the size of a pinhead and white in color. A female bed bug can lay up to 500 eggs over her lifetime, which hatch within 6 to 10 days. The eggs are often laid in clusters in hidden areas such as mattress seams, bed frames, and behind headboards.
Nesting Areas: Where They Hide
Bed bugs don’t only live in beds. Their nesting areas can include:
- Mattress seams and tufts
- Box springs and bed frames
- Cracks in walls or furniture
- Behind wallpaper or picture frames
- Inside electrical outlets or baseboards

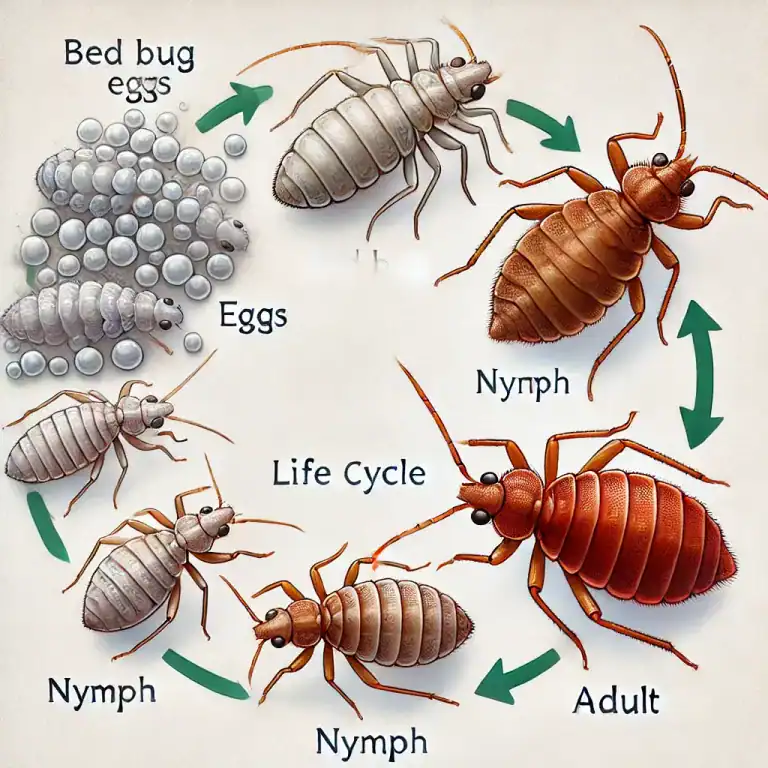
The Life Cycle: Cimex lectularius Metamorphosis
Bed bugs undergo incomplete metamorphosis, with three major stages:
- Egg Stage: Tiny and white, bed bug eggs hatch in 6-10 days.
- Nymph Stage: Bed bug nymphs are lighter in color and must feed on blood to molt and grow. They go through five molts before reaching adulthood.
- Adult Stage: Adult bed bugs are fully grown after their final molt and are ready to reproduce, continuing the infestation cycle.
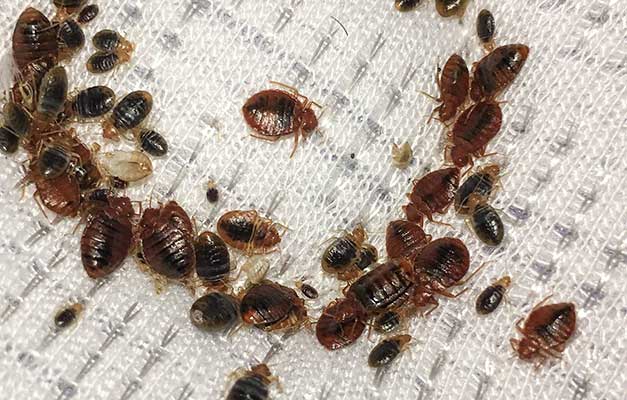
Signs of a Bed Bug Infestation
Common signs of bed bug infestations include bites, bloodstains on bedding, and bed bug droppings (small black or brown spots). Look for these signs in common nesting areas to detect an infestation early.
Why Bed Bugs Are Hard to Eliminate
Bed bugs are notoriously hard to eliminate due to their small size, ability to hide in hard-to-reach places, and rapid reproduction. Professional bed bug control from Pest Dominion is essential to completely eradicate infestations.
Contact Pest Dominion for Bed Bug Elimination
If you suspect a bed bug infestation, contact Pest Dominion today. Our expert pest control services are designed to completely eradicate Cimex lectularius and prevent future infestations.
Visit us at www.pestdominion.com to learn more about our services.



Need Help Getting Rid of Bed Bugs?
Pest Dominion offers professional bed bug eradication and BPCA bed bug control services across Slough and surrounding areas. Our bed bug experts use proven, safe, and discreet methods for lasting results.
📍 Contact Pest Dominion today
📞 07999 936075 | 03308 224460
Don’t wait — get rid of bed bugs before they spread further. We guarantee discreet, reliable, and long-term results.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

